

Fundamentals of information security. What is information security
Table of Contents
Specialists of Falcongaze analytical centre prepared an article that explains the basics of information security. It will be useful to those who wish to begin to get to know this topic. Reading the article, you’ll know
- precise definition of information security
- properties that information and the means of its processing should possess;
- step-by-step list of actions that will ensure information security in the organization.
What is information security
In different documents, scientific and educational literature, you can find many definitions of information security that differ from one another. It is important to understand for those who only begin to study information security, that it is only appropriate to rely on this or that definition if it is relevant to that specific area within which you are studying information security. The definition of information security will be different in compute science, law, sociology, political science.
Approaches to the “Information security” definition
Comparative analysis of various definitions of information security which we can meet in modern-day technical and academic works allows determining three general approaches: statistical, activity-based and complex. Differences between them are displayed in the Table 1.
Table 1
Approaches to the “Information security” definition
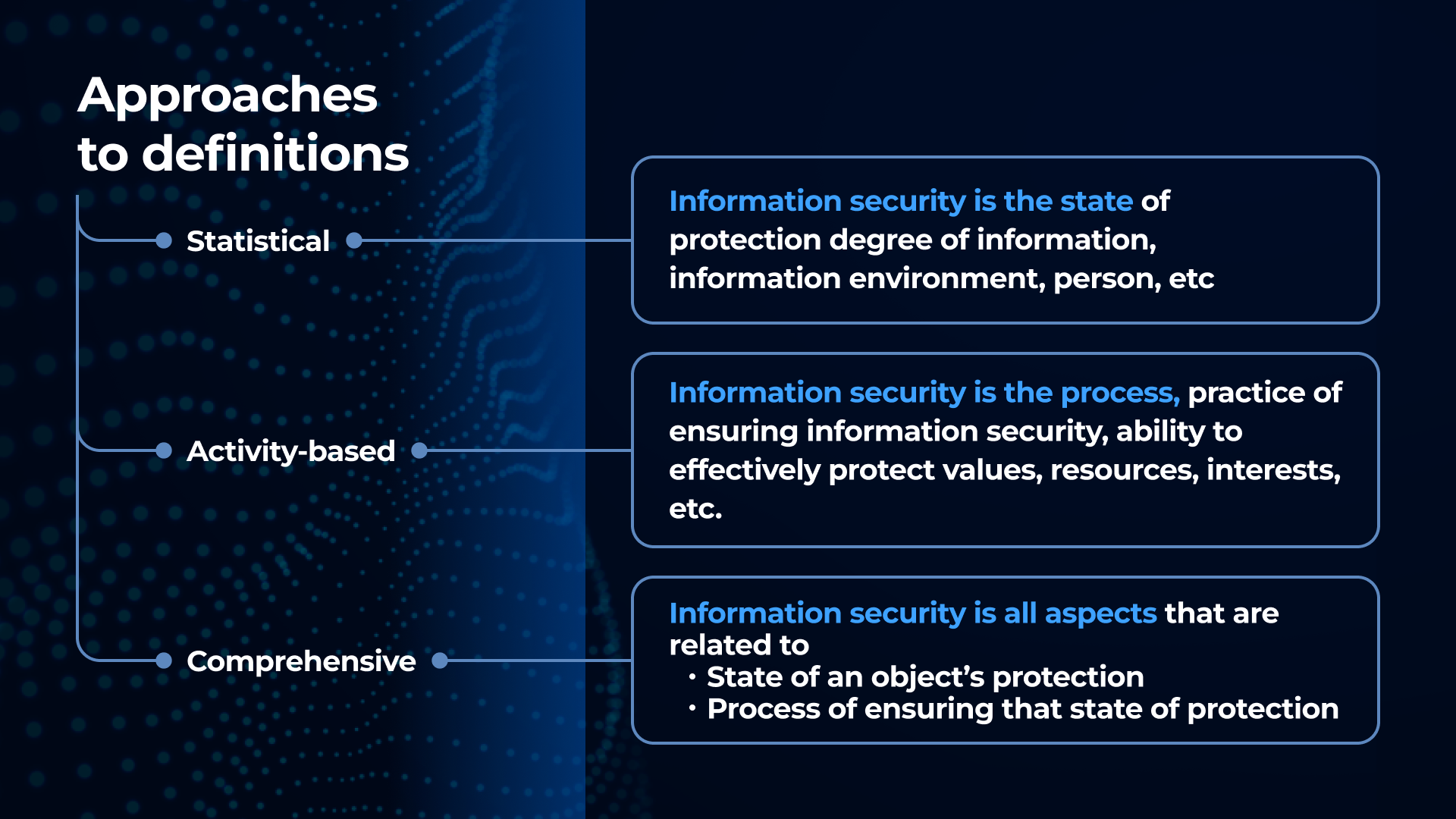
Definitions of information security also may differ depending on the object or field to be considered in the context of cultural, social, political or economic problems. For instance, the researcher may consider information security in state politics, in organizations, in computer science, in society, etc. In this regard, the interpretation of the term can be narrowed, specified.
For example, the new EU Cybersecurity Strategy for the Digital Decade (2020) aims to protect a wide range of economic sectors and subsectors: energy, banking, financial infrastructures, health, waste water, and, what is the most interesting for us, digital infrastructure and digital providers, including internet exchange points, DNS providers, TLD name registries, cloud computing service providers, data centre service providers, content delivery networks, trust service providers, and public electronic communications networks, electronic communications services, online marketplaces, online search engines, and social networking service platforms.
Based on the above, states, IT systems, all social infrastructure, a person itself, their rights can be objects of informational security. Subjects of informational security are people, departments and bodies that act to ensure its aims.
Basic definitions of the term informational security which are correlated to various subjects and areas of life, described among researchers who study this topic from the basics, comprehensively and multidimensionally.
Definition of information security in the legislation of the USA and EU
We consider, that the most accurate definition of information security was set out in 44 U.S.C., SEC. 3542. It is quite wide, but let us firstly focus on the main part.
The term “information security” means protecting information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
The term information security includes the other term, which is no less important – cybersecurity. But nowadays, the borders of these terms have begun to blur. Cybersecurity is formally defined as prevention of damage to, protection of, and restoration of computers, electronic communications systems, electronic communications services, wire [CNSSI4009] [HSPD23].
For example, the laws of the EU often define information security as cybersecurity. However, it should be noted that the EU lacks a clear and unified definition of cybersecurity, which is variously enshrined in regulatory legal acts. Still, we can apply to one of the definitions represented in the law.
Cybersecurity means the activities necessary to protect network and information systems, the users of such systems, and other persons affected by cyber threats (EU Cybersecurity Act, (Art. 2.1).
Difference between information security and cybersecurity
In other words, information security is the prevention of any kind of impact on data, caused by unauthorised intentions to use received information. This applies to all information types and all kinds of risks that involve the loss of integrity, accessibility and confidentiality of information.
Threats to information security can relate not only to digital impact and information in the internet, but to all kinds of information in general. For example, a business solution found as a result of brainstorming, or the scheme of supply, drawn by-hand on paper. In this regard, we can look back at the case of the intentional data leak related to the creation of the first antibiotics in the world.
Oxford scientists Ernst Boris Chain and Howard Walter Florey have been developing penicillin since the beginning of WWII. Due to the war, scientists couldn’t find the right producer for their medicine in Europe, so they moved to the USA to keep on working on the mass production of penicillin. But they had difficulties in exporting the drug material itself. Then scientists found a way out. They poured a fungus solution on their jackets, and they were able to stealthily steal the necessary strain of mould and start real production.
Later Alexander Fleming, Ernest Boris Chain and Howard Walter Florey got Nobel Prize for " the discovery of penicillin and its therapeutic properties in various infectious diseases".
The term cybersecurity, in contrast to the wider definition of information security, applies to all methods of protection PCs, smartphones, tablets, laptops, software, inner and outer channels of information exchange, information storage. Thus, cybersecurity is part of the general information security system. The types of threats against which the cybersecurity tools are used, mentioned in the scheme.
Types of cybersecurity threats:
- Malware (aimed to damage workstations);
- Phishing (a specialized attack aimed at receiving personal data);
- Ransomware (software, aimed to encrypting or blocking access to data);
- DDoS-attacks (planned massed exposure to security system);
- Social engineering tools (psychological pressure and negative influence on workers to implement malicious actions);
- Software for cryptojacking (usage of workstations for unauthorized mining on the device);
- AI-attacks (with the use of artificial intelligence tools) and others.

Information properties
As mentioned before, the wide definition of information security in US legislation shows us the properties information security must possess.
Information security is the protection of information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction in order to provide confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Here we are relying on the USA’s definition because, as researches show, nevermind the wide EU legislation base in information security and data protection, the common approach to the term cannot be seen.
Table 2
Information properties
According to FISMA, information must have the next three properties.

These standards shall apply to all information and all kinds of information which does not apply to exceptions.
What is confidentiality
Confidentiality, defined by FISMA, means preserving authorized restrictions on access and disclosure, including means for protecting personal privacy and proprietary information.
A loss of confidentiality is the unauthorized disclosure of information.
What is integrity
Integrity is guarding against improper information modification or destruction, and includes ensuring information nonrepudiation and authenticity.
A loss of integrity is the unauthorized modification or destruction of information.
What is availability
Availability is ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of information. A loss of availability is the disruption of access to or use of information or an information system.
Thus, the whole information security and cybersecurity actions and measures are taken to ensure these three main objectives of any information that circulates in state, society and economic.
Information security institutions in USA and EU
In the information security definitions that we have considered before, there are two processes registered: protection and providing. From this, it is possible to get a general idea of what needs to be done to ensure information security in an organization, for example.
In the USA and the EU specific laws regulate the actions of agencies maintaining information security and controlling the maintenance and fulfilment of legal requirements. In the USA information security is ensured by bodies named in FISMA (44 USC) as agencies. Agencies may be presented as executive departments; a military department; an independent establishment and a wholly owned government corporation. Using information security systems, agencies and departments must provide information security protections commensurate with the risk and magnitude of the harm resulting from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
ENISA in turn is a centre of network and information expertise. It works closely with EU member states and commercial organizations to provide cybersecurity advice and guidance. ENISA also supports the development and implementation of EU policy and law related to national information security. The activities of ENISA consist not only of monitoring the implementation of legislation in the field of information security. ENISA performs educational, coordination, and research functions, in particular, issuing checklists, studies, and other documents.
Types of information in the information security context
For full-fledged ensuring of information security, we need to take into consideration all variety of information types. Commonly, information is divided to the following types.
- By the way of perception
- auditory;
- olfactory;
- tactile;
- visual;
- gustatory.
- By the way of transmission (way of replay)
- Text
- Graphic
- Vibration
- Video
- Numeric
- By intended purpose
- mass (mass media, radio, television, etc.);
- commercial (production secrets, customer databases, original technological solutions);
- personal (information about a particular person and their data);
- specialised (technical, scientific and educational, etc.);
- state (state secrets, specialised decrees, secret orders).

For building an effective information protection strategy it is necessary to realize, through which communication channels it can be transmitted, in what form it will be, how much of this data is confidential.
Here is an example. A privately held software company is interested in keeping its production secrets. Security department in advance thought through the plan for information security and, before the official meeting with strategic partners, checked up on the meeting room for availability of special wire devices (which means, security department considered the possibility of the unauthorized spread of audio information). But audio information is not the only type of information that could be leaked during negotiations. The security department did not foresee that modern technologies allow to track acoustic channels and decrypt audio by vibration of objects in the room. Besides, big windows in the room did not prevent surveillance on the meeting members.
Or another example.
The pharmaceutical company is concerned with ensuring a decent level of protection for commercial information. Company management decided to implement DLP-system. The security department made sure that the system’s rules of security were set, taking into account the production need for constant exchange of files between departments and potential clients. At the same time, the company prohibited the distribution of already signed official documents via the network. An unscrupulous employee in the accounting department decided to discredit his boss in the face of his subordinates and distributed a signed form with the department's salaries and bonuses to the departments, creating an unhealthy atmosphere in the team and leading to several dismissals in the team. This could have been prevented if the security department had set up the rules correctly (taking into account graphical information), or the DLP system itself may have been insufficiently agile and not able to recognize all variants of content analysis.
Ensure information security in organization with Falcongaze SecureTower
To implement the list of actions from above, various methods and ways of ensuring information security, and their combinations can be realized in a particular class of software products named DLP. One of the best DLP-systems today is Falcongaze SecureTower. It has been on the market for 18 years now, developed by advanced specialists and analysts, taking into account all the specifics and conditions of doing business in the Europe and the USA, as well as the minimum technical requirements necessary for implementation.







.png)





